In your modern-day company, chances are you’re already looking for effective KPIs to monitor customer success. Customer success is crucial because most businesses, especially in the software corner, run on a recurring revenue model.
But precisely which KPIs should you be tracking? Why does customer service matter so much for your business? How can you make the most of the KPIs to drive your customer success and employee performance?
First, there needs to be a streamlined pattern of KPIs. Companies’ needs differ, and how they measure their customer success is unique. Hence, your KPIs will likely be different from the ones other businesses use.
It is also true that businesses have to, most importantly, drive the best value for customers to keep their net scores afloat. And the foolproof way to do that is through customer success KPIs. While they may differ from business to business, there are plenty of KPIs right now that overall assess customer satisfaction and maximize retention.
And, they’re adaptable for generally all businesses.
What are Customer Success KPIs?
Customer success is a term for a business initiative with the primary goal of ensuring that customers draw the maximum value out of a brand’s product. The whole objective of this initiative is to ensure that the customers attain their goals and desires behind purchasing your product.
If businesses can attain this level of customer satisfaction, it will mean that the latter will not churn. But then, how can you measure customer success?
If it were for a single customer, asking if they’d met what they wished to achieve with our product would be easy. But since it’s a large group of customers, we’d have to measure the success collectively. And how can businesses do that? By diving into data, of course.
This is where the key performance indicators are most crucial in customer success. They’re the metrics that help companies measure, define and track progress in their initiatives. Below, let’s look at the five KPIs every business can use to monitor customer success.
1. Customer LTV
LTV stands for lifetime value statistics of customers, which are helpful for analyzing the cost vs. benefit. It also factors in the user acquisition cost, and one can calculate this by a simple formula. All you have to do is multiply your total number of customers by the average earning you make off every customer each time. Mobile marketing and retention firm CleverTap, breaks it down in the following infographic.
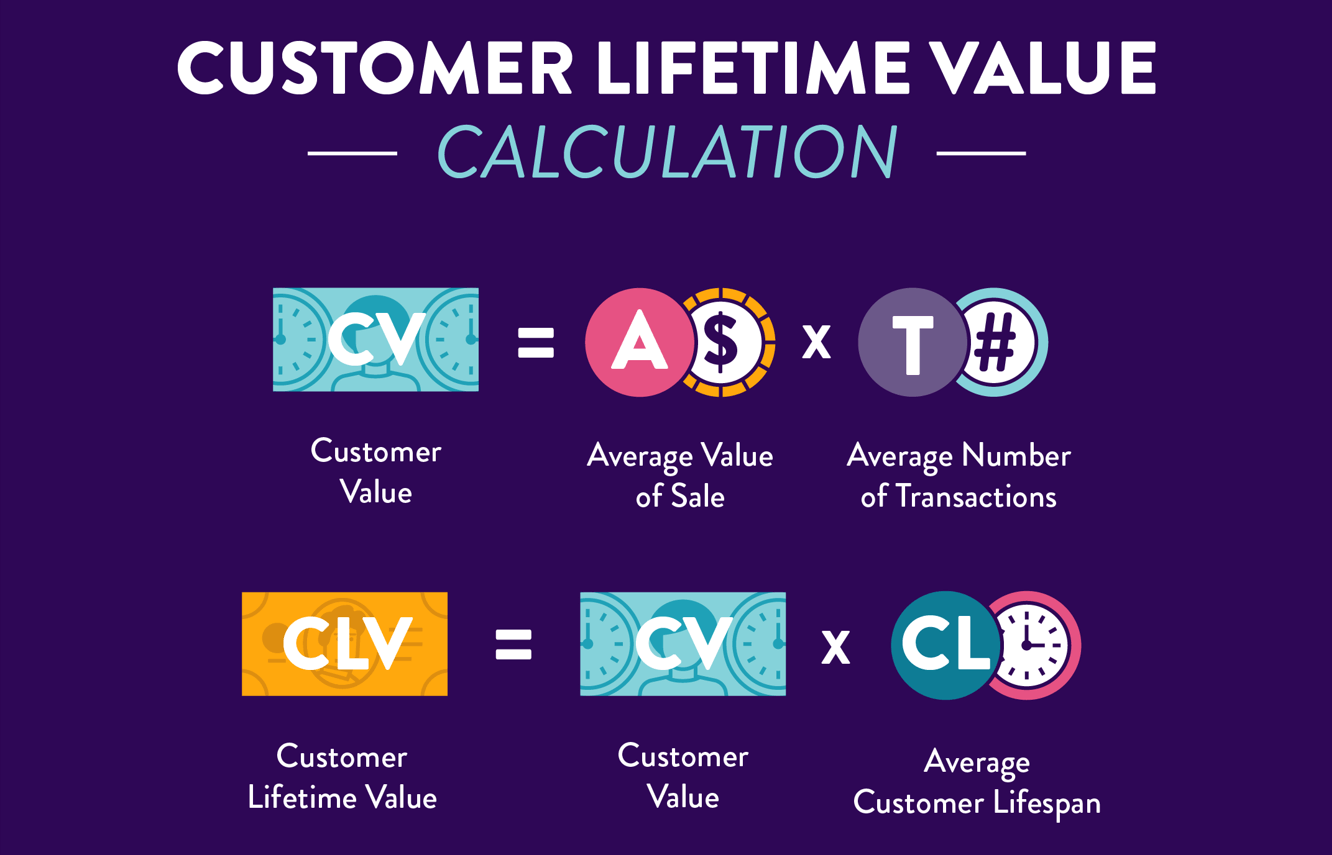

There are more uses to customer LTV than this. For instance, if you manage to boost the value of the product you’re selling in different ways, you will simultaneously see your customer LTV increase.
Perhaps a good way to do so is to add more appeal to your product tiers categorized as “highly-priced.” This will help you upsell the goods, but there’s more to it. If your upsells comprise a la carte items, rather than just the goods from the high-priced tier, making them more appealing for your customers through innovation will boost your upsells too.
Through this strategy, you will offer something of greater value to customers. When your customer LTV goes up, it means the satisfaction level of the customers has increased as well.
2. Churn
You may already know the churn rate as the average percentage of customers that abandon your brand every month. But apart from this churn, there’s something else that deserves your attention to.
If your high-tiered customers are converting to low-tiered products at an alarming rate, it is likely a sign that your high-tiered goods are falling short of delivering the value you promised. If customers do not get what they expected from your product, chances are they’ll ditch the high-tiered offerings and settle for something else.
This is also a churn commonly known as “gross dollar churn.” Hence, when calculating how customers weigh the value of products you offer, it’s essential to be mindful of the gross dollar and customer churns.
This KPI makes you aware of the class of customers that is abandoning you more frequently and identifies the problem causing it.
3. Onboarding
Customer support teams measuring success consider the engagement of customers as their first step in the entire process of onboarding. Teams that work on product-oriented growth typically have automated onboarding sequences.
Hence, they measure how customers have completed the onboarding sequence using the automated data. Moreover, the teams can measure the average time needed for new customers to see the onboarding process to a successful end.
4. Quarterly Renewed ARR
The ARR is “annual recurring revenue,” a common metric in subscription revenue and SaaS businesses. However, since a large percentage of businesses work on the recurring revenue model, this KPI metric is also useful for all of them.
So managers responsible for handling customer success can delve deeper into the satisfaction quotients by using “Quarterly renewed ARR.” This KPI refers to your business’s annual revenue percentage in each quarter.
Now if we were running our businesses in the ideal universe, this revenue percentage would be 100%. This would have meant that all our existing customers found the value they expected, continued subscribing, and no churning occurred. But alas, the reality is different.
Since we don’t live in a fantastical world, the ideal revenue percentage should be 90% and onwards. The ultimate goal should be to reach positively expanding numbers.
5. NPS: Net Promoter Score
The NPS metric is useful for showing you the level of loyalty you enjoy from your customers. It points you to the ones who are your fans and promotes your brand voluntarily. It also reveals the customers that could drive prospective buyers away from the brand.
Taking a net promoter score survey is a good start to using this KPI. You will have to ask your customers just one question in this survey, which is:
“How likely are they to recommend your brand to family or friends?”
You can provide a scale of 0 to 10 for your customers to answer and the likelihood of them recommending your brand to others. This is how the scores would read:
- 0-6 means the customers are detractors. They’re the unhappy ones who have a higher tendency to keep prospective buyers away from your brand.
- 7-8 are passive buyers. They’re the lot that is satisfied with the products and services they avail from you but too passive to promote you to others. Don’t expect word-of-mouth advertising from them.
- Then comes the 9-10 scoring, which means a loyal fan following. They love your brand, engage enthusiastically with you, are satisfied with your products and services, and will surely recommend your brand to others.
Using the NPS metric, you can use your customer feedback for your business strategy. Moreover, it’s relatively easier to calculate and is a great way of discovering how happy or unhappy the customers are with you.
Why Businesses Need to Use Customer Success KPIs
1. Relentless Support
The market is becoming an increasingly competitive landscape for businesses to survive. A company must rely on something other than its customer support team to stay ahead of its customer issues. More help is required, and KPIs for customer success provide just that.
These metrics help teams go higher, enabling customers to proactively derive a thoroughly exceptional customer experience from the brand’s products and services.
2. A Bird’s-Eye Growth View
Happy and satisfied customers are the backbone of a company that wishes to grow. There’s no denying that customers hold the power to make or break a brand’s reputation in the marketplace.
If you use KPIs, they help you keep a watchful eye on customer success. Consider KPI metrics as an effective way of gauging the pulse of your customers at any given moment.
3. Decisions Supported by Data
Without the help of KPIs, what would companies have on hand? Nothing more than intangible data. But when KPIs come into action, the same intangible information converts into something quantifiable and far more substantial.
Trust us; these inferences are useful in making core strategic decisions for the company’s healthy future. For instance, with KPIs for customer success, you can better analyze your customers’ behavior. This helps you refine your support responses, especially during complaint resolution.
Final Thoughts
Key performance indicators for customer success are the backbone of every successful company. The simple truth of today is that companies that use KPIs effectively for measuring customer success measure performance fairly well. Most importantly, those companies plan their goals and execute them more successfully.
The top five KPI metrics for customer success are a good place to start, and with consistent use, will help take your organization to better performance levels.







